Potatoes play an indispensable role in the kitchen of vegetarian dishes, with their diverse shapes, textures, and flavours making them a favourite among plant-based cuisines. Potatoes are an ideal substitute for traditional main courses, with a moderate texture that allows them to be shaped into various forms such as mashed potatoes, potato cakes, and fries. These varied forms provide a colourful array of options to complement various vegetarian main dishes, bringing a rich and diverse selection to the dining table.
Nutritional value
A starch-rich potato is low in calories. It has a great nutritional value. Potato is high in fibre. It also has various minerals and vitamins, especially potassium and vitamin B. There are more than 300 types of potatoes in the world. Potato skins come in a variety of colours, yellow, pink, red, blue, purple and black. Common colour in the market are usually yellow, red or purple. Purple and blue potatoes contain Anthocyanin. Purple and red potatoes contain more antioxidants relatively than the others.
Potatoes are an excellent source of carbohydrates, providing the body with essential energy. Additionally, their rich dietary fibre content contributes to maintaining digestive health and promoting a sense of satiety. Potatoes contain abundant vitamins and minerals, such as potassium, making them a low-fat, high-water content ingredient suitable for health-conscious vegetarians, contributing to maintaining balanced nutritional intake.

Common media of plant-based ingredients
Potatoes have excellent flavour absorption, serving as an excellent base for vegetarian dishes by fully soaking up the essence of seasonings. Their simple flavour makes them highly adaptable, allowing them to complement a variety of seasonings, thus creating rich and flavourful vegetarian dishes. Additionally, potato mash possesses the ability to shape food. Whether molded into patties, nuggets, or cutlets, the texture and pliability of potato mash provide a foundation for innovation and visual appeal. In vegetarian meat recipes, potato mash acts as an outstanding binding agent. Its sticky consistency helps tightly hold ingredients together, ensuring cohesion during the cooking process—a unique quality that is indispensable in crafting delicious and cohesive vegetarian alternatives.
Potatoes can be prepared through various cooking methods such as baking, frying, boiling, or steaming, resulting in different textures and flavours. This adaptability makes potatoes suitable for various culinary styles, from light salads to hearty stews, showcasing their unique advantages.
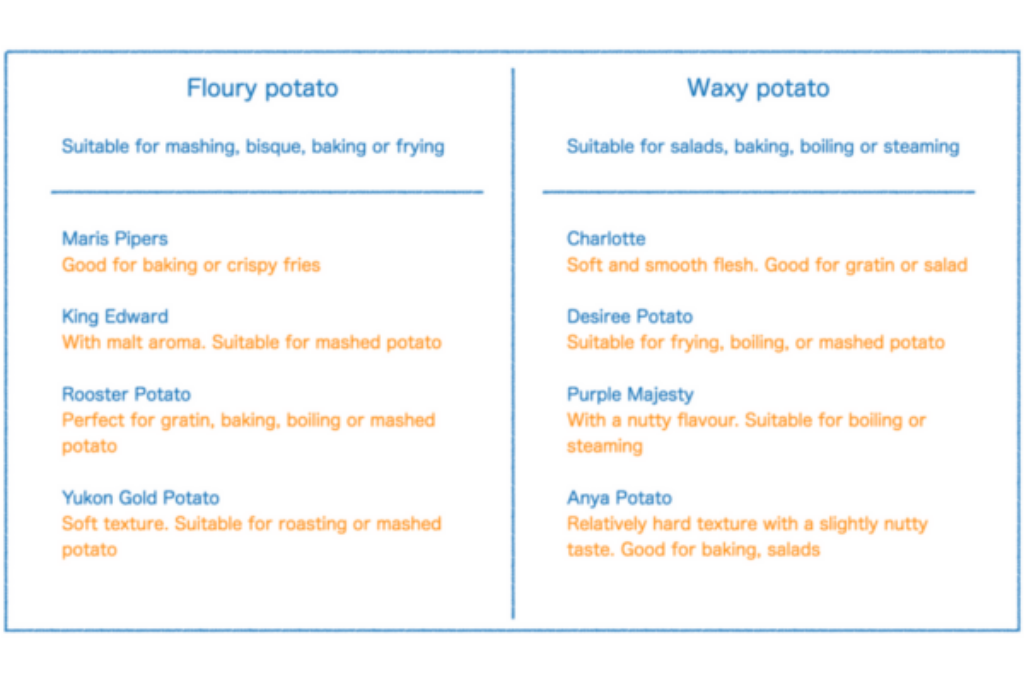
Different potatoes for different textures
Potatoes are categorised generally into 2 groups – floury potato and waxy potato
Unlock the secrets to perfectly fluffy mashed potatoes
Creating fluffy mashed potatoes involves a series of scientific principles, from the starch structure of potatoes to the appropriate moisture and mixing processes that impact the final texture. Firstly, selecting the right potato variety is crucial. Opting for varieties with high starch content is ideal, as starch undergoes gelatinization during cooking, providing structure and fluffiness.
The starch in potatoes begins to gelatinize when heated, forming a sticky structure. Proper water temperature and time during boiling are critical to ensure complete starch gelatinization while avoiding excessive thickness. As potato mash is stirred during the preparation process, starch further gelatinizes, forming a more stable structure, contributing to increased stickiness and fluffiness.
Adding sufficient liquid and fat is essential to crafting fluffy mashed potatoes. Adequate addition of liquid (usually milk or butter) and fat helps make the mash more moist and fluffy. Moisture contributes to gel formation with starch, while fat prevents excessive stickiness during mixing.
While stirring, it is crucial to avoid over-mixing. Over-mixing excessively disrupts the starch gel structure, leading to loss of elasticity. Therefore, caution and avoiding prolonged or excessive stirring are essential. After completing the potato mash, keeping it appropriately warm helps maintain its fluffiness. Placing the mash in a warming tray or a warm environment aids in preserving its fluffy texture.
Through these scientific principles, you can create finely textured, fluffy, and delicious mashed potatoes. In summary, the role of potato mash in vegetarian cuisine goes beyond the conventional; it becomes a culinary artist’s media for shaping and enhancing plant-based creations. Its formative abilities, binding prowess, and transformative nature make it an indispensable ingredient in the quest for crafting savory and visually stunning vegetarian delights.
In addition, there is a hint that we make potatoes for salads. It should be cooked in water below 60 oC, so that the shape of the potatoes can keep. It is tasty.
Reference
“The Science of Cooking”, written by Stuart Farrimond, published by DK publication







